Ans-
Construction —
Photocell consists of evacuated glass tube containing two electrodes emitter (K) and collector (A).The emitter is shaped in the form of a semi hollow cylinder. It is always kept at a negative potential.The collector is in the form of a matal rod and fixed at the axis of the semi-cylinderical emitter. The collector is always kept as a positive potential.The glass tube is fitted on non-metallic base and pins are provided at the base for external connection.
Working —
The emitter is connected to negative terminal and collector is connected to positive terminal of a battery.A radiation of frequency more than threshold frequency of material of emitter is made incident on the emitter. Photo-emissions take place. The photoelectrons are attracted towards the collector which is positive w.r.t the emitter. Thus, current flows in the circuit.If the intensity of incident radiation is increased, the photoelectric current increases.
2) Explain Maxwell distribution of molecular speed with necessary graph.
Ans-
Gas is collection of tiny particles separated from one another by large empty spaces and moving randomly in all directions. In the inter course of their motion, they collide with one another and also with the walls of the container. Due to these collisions, the speed and the direction of motion of the molecules keep on changing. Although. it is not possible to find out the speeds of the individual molecules, yet from the probability considerations it has become possible to work out the distribution of the molecules.
This distribution is referred to as Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
The distribution of speeds remains fairly constant at a particular temperature althought the individual speeds of the molecules can change.
Maxwell plotted the fraction of molecules having different speed against the speeds at particular temperature. This plot is shown as follow:

Improtant feature of this curve are:
The fraction of molecules with very low or high speeds is very small
The fraction of molecules possessing higher and higher speeds goes on increasing till it reaches a peak and then starts decreasing
The maximum fraction of molecules possesses a speed, corresponding to the peak in the curve which is referred to as most probable speed
The area under the curve gives the total number of gas molecules.
3) State and Prove the law of conservation of angular momentum
Ans-
The quantity of rotation of a body, which is the product of its moment of inertia and its angular velocity.
Law:-
Principle of conservation of angular momentum states that, If no external torque acts on a system, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant. If I be the moment of inertia of a body about a given axis of rotation and w be its angular velocity, then I w = constant.

4) Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
Ans-
Diamagnetic Ferromagnetic
Substance Substance
1)Weakly repelled 1)Strongly
by a magnet attracted by a
magnet
2)When kept in a 2)When kept in a
non-uniform non-uniform
magnetic field, it magnetic field ,
shows moderate it shows strong tendency to move tendency to move from stronger to from weaker to
the weaker part the stronger part
of the field. of the field.
5) State Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
Ans-
Kepler’s first law (Law of orbit):
Every planet revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit with the sun situated at one of the focii of the ellipse
Kepler’s second law (Law of equal areas):
The radius vector drawn from the sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time, i.e., areal velocity of the radius vector is constant.
Kepler’s third law (Law of periods):
The square of the period of revolution of the planet round the sun is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the elliptical orbit
6) Four resistances 4Ω,8Ω,XΩ, and 6Ω are connected in a series so as to form Wheatstone’s
network. If the network is balanced, find the value of ‘X’.
Ans-
R1 = 4Ω, R2 = 8Ω, R3 = XΩ, R4 = 6Ω
When Wheatstone’s network is balanced,
R1/R2=R3/R4
4/8=X/6
∴ X = 3 Ω
The value of ‘X’ is 3Ω.
7) Define an ideal simple pendulum. Show that, under certain conditions, simple pendulum performs linear simple harmonic motion.
Ans-
In practice a small but heavy sphere can be regarded as point mass and a light string whose weight is negligible compared with weight of the bob can be taken as a weightless fibre.
Suppose that a simple pendulum of length ‘L’ is displaced through a small angle θ and released. It oscillates two sides of its equilibrium position. At displaced position, force acting on the bob are (1) its weight mg (2) the tension T in the string. Resolved ‘mg’ into two components ‘mg sinθ’ to ⊥ the string and ‘mg cos θ’ parallel to
the string. The component ‘mg cos’ is balanced by the tension in the string. The
component ‘mg sinθ’ is unbalanced. This acts as restoring force.
F = - mg sinθ -ve sign indicates that force is opposite.
But θ is very small , sinθ = θ
`F=-mg theta and theta =X/L`
`therefore F=-(mgX)/L`
`F=-((mg)/L)X`
But `F=ma_"cc"`
`therefore ma_"cc"=-((mg)/L)X`
`a_"cc" =-(g/L)X`
`a_"cc" alpha (-X)`
The motion of simple pendulum is linear S.H.M.
`a_" cc" =-(g/L)X`
Condition for simple pendulum: (1) Bob must be small but heavy sphere.
(2) It must be suspended by light string.
(3) It must be supported by rigid support.
(4) Amplitude must be very small.
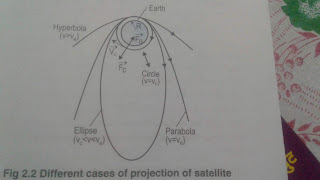
8) Draw a diagram showing different stages of projection of artificial satellite
Ans-
An artificial satellite is a man made objects
9) State the law of radioactive decay. hence derive the relation N = Noe-λt . Represent it graphically.
Ans-
Radioactive decay law :
The number of nuclei undergoing the decay per unit time is proportional to the number of unchanged unclei present at that instant.
Proof:
Let ‘N’ be the number of nuclei present at any instant ‘t’.Let ‘dN’ be the number of nucleic that disintegrated in short interval of time ‘dt’.According to law
`(-dN)/dt ∝ N`
`therefore (dN)/dt= -λ N`........................(1)
Where λ - decayconst
`therefore(dN)/N=-λdt`
`therefore \text{integrating both sides}`
`∫ (dN)/(N)=∫-λ dt`
` \[\ell\]N= λ t+C `................................(2)
Where C → integration consta

∴ at t = 0 , N =N0
∴ \[\ell\] nN0 = C ......... .. 3
`therefore ` Frome equation (2) and (3)
`l n N = -λ t +`\[\ell\] `nN_0`
`λ t = In\ N - In\ N_0`
-λT= In `(N/N_0)`
`N/N_0= e^-(λt)`
`therefore N=N_0e^-(λt)`
10) Explain what is Doppler effect in sound and state it any four application
Ans-
●The Doppler effect is the apparent shift in wave frequency due to the movement of a wave source.
● The Doppler effect explains why we perceive a change in pitch of the sound of siren when we see an ambulance approaching towards us.
●It also explains the presence of shock waves and sonic booms when observing a supersonic aircraft.
Applications of Doppler Effect
■Sirens
■Radar
■Astronomy
■Medical Imaging
2 nd part is coming soon . Subscribe for read the comming posts.
Share with your Friends for good marks
Thankyou 😊
Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.